Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Biotech: Revolutionizing Medicine Development
Increasing Efficacy and Speed and Reducing Cost
Several of the Aescap portfolio companies in both the Aescap Life Sciences and Aescap Genetics fund have an internal team with hundreds of AI experts. Is this just a hype or is there a real added value? And what are they aiming for?
AI-Powered Medicine Discovery
The traditional medicine discovery process is often lengthy, costly, and requires extensive trial and error. AI, however, has emerged as a game-changer in this field. Many pharmaceutical and biotech companies have embraced AI to accelerate and streamline their research efforts. AI-powered platforms enable the screening of millions of products, predicting their efficacy and safety. This accelerates the initial stages of medicine discovery, reducing the time and resources needed to bring new medications to market. Additionally, AI can optimize existing medicines by identifying new applications, dosages, and combinations, leading to a higher success rate in clinical trials. Therefore, AI is reducing costs of medicine development and as a result will lower the prices of new medicines.
Enhanced Diagnosis and Personalized Treatments
AI’s potential to revolutionize healthcare extends beyond medicine discovery. Machine learning algorithms can process complex patient data, including medical records, diagnostic imaging, and genetic profiles, to support early detection and accurate diagnosis of diseases. By leveraging this technology, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions and deliver personalized treatments tailored to each patient’s unique characteristics.

Moreover, AI-powered systems can analyse genetic data to identify genetic markers associated with specific diseases or medicine responses, increasing the chances of successful outcomes and minimizing adverse reactions.
AI at Aescap’s Portfolio Companies
A recent survey conducted among our portfolio companies reveals that the majority have embraced AI for a multitude of reasons. Almost all of these companies have established robust in-house AI teams to drive their initiatives forward. Or have sought the expertise of specialized external AI biotech consultancies, which currently number around 180 worldwide. One of them, Schrodinger Inc, now sell their services to over 800 biotech companies.
Sophia Genetics
Aescap Genetics’ portfolio company Sophia Genetics mission is to build the future of AI-assisted medicine. They’re integrating multimodal healthcare-omics data, unlocking existing data silos and developing machine learning models to produce actionable insights that could eventually support healthcare professionals to improve patient outcomes.
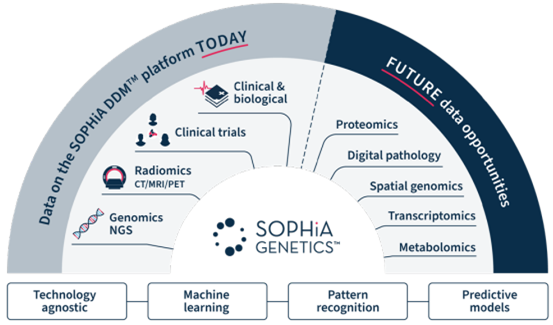
AI at Sophia Genetics
Sophia Genetics is selling their AI derived enhanced diagnostic services to around 800 hospitals globally. The company so far focused on the enhancement of diagnosis in oncology and inherited disorders. For this it’s vital to combine genomic and phenotypic information to support discoveries, treatment decisions, and medicine development efforts. Sophia Genetics aim to broaden their services to many other disease areas such as cardiology and neurology.
The first pharma companies have found their way to Sophia Genetics. One of their larger clients is AstraZeneca. Their aim is to accelerate clinical trials, support evidence generation for market access, and improve clinical decision-making. Helping clinicians to select the best possible treatments.
Evotec
Evotec is using machine learning and AI tools to predict and improve manufacturability of protein based medicines as well as cutting-edge technologies to optimize manufacturing processes. Properly optimized medicine products and manufacturing processes that are easily scalable are key to lower manufacturing costs and thus make important contributions to providing innovative medicines at affordable prices to patients.
Evotec is working on personalized, preventive and predictive approaches, using intelligent, data-driven technologies and platforms, to accelerate access to more precise and effective medicines.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential, the integration of AI in medicine development also presents challenges and ethical considerations. The reliance on algorithms raises concerns regarding transparency, accountability, and potential biases within the decision-making processes. Safeguarding patient privacy and ensuring the secure handling of sensitive medical data are critical aspects that require stringent regulations.
AI is Shaping the Future of Medicine
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing medicine development. It’s definitely not just a hype, but here to stay. When used wisely AI holds a tremendous added value. For patients, doctors, biotech companies and also for us as stock pickers. With AI’s power to revolutionize healthcare, we are witnessing a paradigm shift that will shape the future of medicine.
AI at Aescap
Also at Aescap AI is used more and more. In our due diligence, in defining the momentum of our (future) portfolio companies and as a sparring partner on endless other subjects.
Jefferies: Areas AI could Transform Biotech over 10 Years
Biotech analysts of investment bank Jefferies shared their predictions on what AI might/will accomplish for patients, doctors and biotech companies in particular.
- AI will identify the genetic risk factors in diseases which are caused by multiple genetic mutations.
- AI can predict or know all the complex biochemical systems and connections in the human body and come up with novel targets to treat a disease.
- AI will then come up with and generate a novel, for example protein based medicine, and structure from scratch to have a desired function. E.g.: “Build me an extended half-life protein that can transport this enzyme to shut down this receptor”.
- AI can model ligand/receptor interactions to find the best small molecule compound medicine.
- AI can fully replicate (from enough datapoints) animal models and organ models to replace their role or requirement in preclinical tests to cut years off testing.
- AI will then find the best subset of patients for the medicine which benefit most from the medicine.
- AI will provide specific prognostic information to diagnose and treat the patient better than a doctor. “Given the patients treatment history and tumor biology, what is the prognosis?” “Looking at the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and other datapoints, this patient is unlikely to respond to this medicine but should response to this one.”
- AI will be able to improve manufacturing and yield and identify factors affecting output and yield.
- AI can predict genotype and phenotype of a human species taking into account all the regulatory mechanisms in the body and based on genetic sequences submitted from parents.
Glossary
- A ligand is a molecule that binds to a receptor, typically a protein, to initiate a biological response. In the context of medicine discovery, a ligand refers to a small molecule compound that interacts with a specific target protein.
- A receptor is a protein located on the surface or inside a cell that recognizes and binds to specific molecules, such as ligands. The binding of a ligand to its receptor often triggers a signaling cascade or other biochemical processes.
- Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual organism. It represents the specific combination of genes an individual possesses. The genotype encompasses all the genes present in an individual’s DNA. Genotype determines the potential range of traits and characteristics that an individual can inherit or pass on to offspring.
- Phenotype refers to the observable traits or characteristics of an individual resulting from the interaction between the genotype and the environment. It represents the physical expression or manifestation of the genes. Phenotypic traits can include physical features like height, hair color, eye color, and facial features, as well as physiological traits such as metabolism, blood type, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Additionally, behavioral and cognitive traits, such as intelligence or temperament, are also part of the phenotype.